Search
Important contacts
Technical
support
support
VLAN – Virtual Local Area Network
7/23/2008
These days, it would be hard to imagine the configuration of the local networks without utilization of VLAN, which means the Virtual Local Area Network. What actually VLAN means, what are the types of it, and why is the VLAN being used?
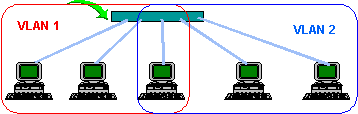
The main reason for VLAN usage is the possibility to perform segmentations of the devices/ports within the network, like the routers at the lower level of ISO/OSI model. Therefore, via utilization of VLAN, we can separate the device or service connected within the network using switches. Another benefit is an option to connect the devices between each other within the large distance. The types of VLAN can be segmented according to their method of marking. The port-oriented VLAN is the first option to perform the configuration within the management of the active elements called WebSmart. All the packets are being received, which come in or come out through the optional VLAN network port. The VLAN networks based on ports are subject to no filtering criterion. The only criterion is the actual physical port, to which the device is connected. Such VLAN can be for example the PVLAN-1 and it can contain the members of the ports 1, 2, 3, and 4. If the device is connected to the port 1, it will be able to communicate with the ports 2, 3, and 4. If another device is connected to the port 5, the communication among the optional port in PVLAN-1 will not be possible. The name of the group must be assigned to all VLAN networks based on ports. The switch is supported usually by the number of the VLAN port networks, which corresponds to their number of ports.

The marked VLAN networks are another option. These can be configured within the scope of L2 management and they can be expanded outside of a single active element, as is the case of the VLAN networks based on ports. The VLAN networks based on marks assign their members according to the VID identifier. This principle is significantly different from the VLAN networks based on ports. If the other rules are present in the list of the input or output filtering, the control of the packets will be conducted using other filtering criteria, which will decide whether they can be transmitted further or not. It is necessary to assign the name of the network and the VLAN identifier to the all created VLAN networks based on marks. The valid VLAN identifiers belong to the range of 1–x, where "x" is the maximum number of supported VLAN networks.
A Symmetric VLAN is the input rule (the rule 1 – the input filtering rule 1 is "transmit further only those packets, which have their VID identifier corresponding to the configured VID identifies of this port"). For example, if the port 1 accepts the marked packed with VID = 100 (VLAN network name = VLAN100), and simultaneously the Symmetric VLAN function is enabled, the switch will check whether the port 1 is the member of the VLAN100 network. If positive, the accepted packet is transmitted further.
 Otherwise the accepted packed is dropped. In the case of the Symmetric VLAN, all VLAN networks use the same filtering database for storage of information on the membership within the VLAN networks. This database enables an option to find or search the information on the membership within the VLAN network.
Otherwise the accepted packed is dropped. In the case of the Symmetric VLAN, all VLAN networks use the same filtering database for storage of information on the membership within the VLAN networks. This database enables an option to find or search the information on the membership within the VLAN network.
The marked VLAN networks are another option. These can be configured within the scope of L2 management and they can be expanded outside of a single active element, as is the case of the VLAN networks based on ports. The VLAN networks based on marks assign their members according to the VID identifier. This principle is significantly different from the VLAN networks based on ports. If the other rules are present in the list of the input or output filtering, the control of the packets will be conducted using other filtering criteria, which will decide whether they can be transmitted further or not. It is necessary to assign the name of the network and the VLAN identifier to the all created VLAN networks based on marks. The valid VLAN identifiers belong to the range of 1–x, where "x" is the maximum number of supported VLAN networks.
A Symmetric VLAN is the input rule (the rule 1 – the input filtering rule 1 is "transmit further only those packets, which have their VID identifier corresponding to the configured VID identifies of this port"). For example, if the port 1 accepts the marked packed with VID = 100 (VLAN network name = VLAN100), and simultaneously the Symmetric VLAN function is enabled, the switch will check whether the port 1 is the member of the VLAN100 network. If positive, the accepted packet is transmitted further.
Login
If not specified prices are without VAT in EUR.

